Details
Views:
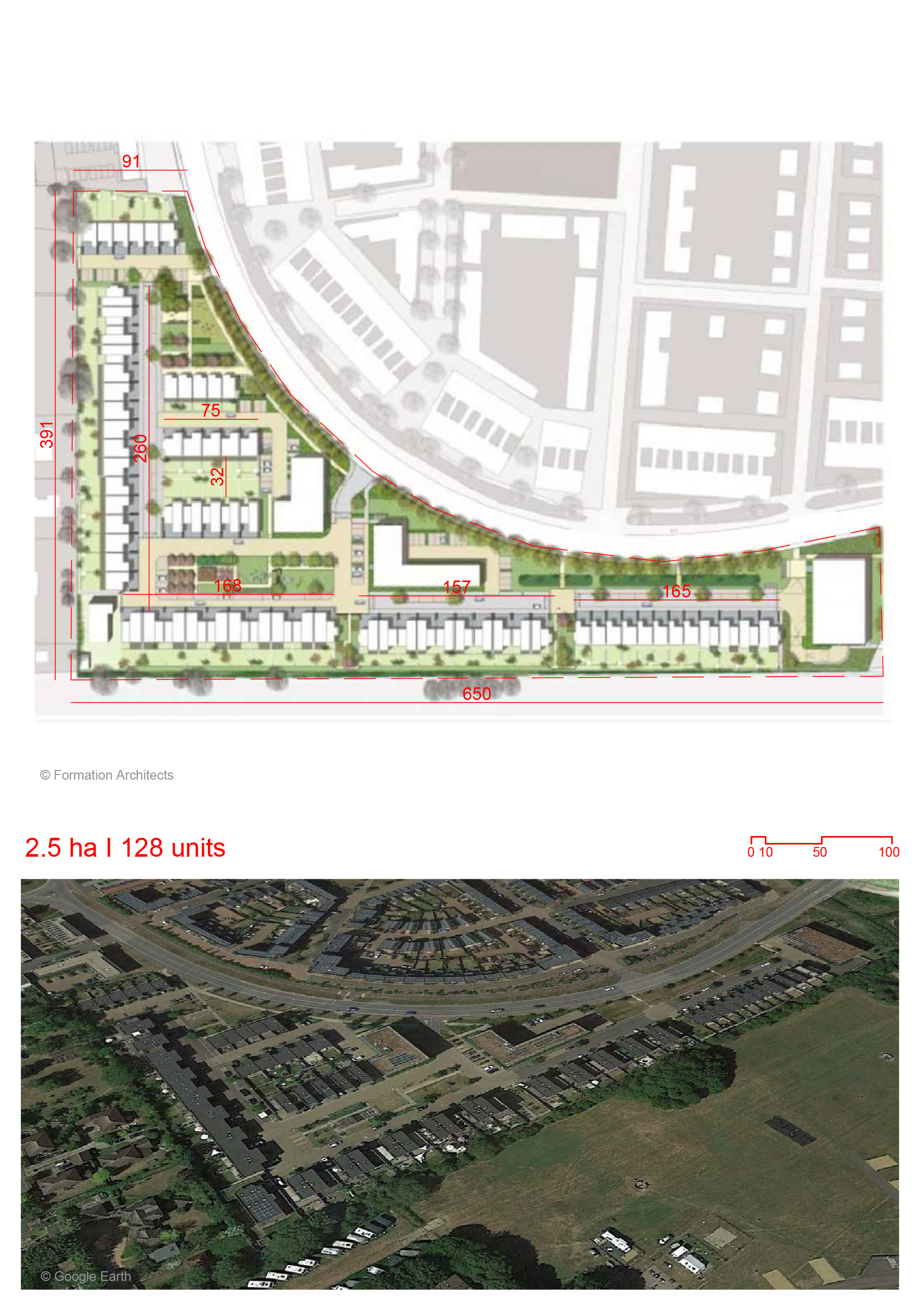
650
Tags
Data Info
Author
IWONA BUCZKOWSKA
City
Seine-saint-denis
Country
France
Year
1993
Program
Wooden Co-housing
Technical Info
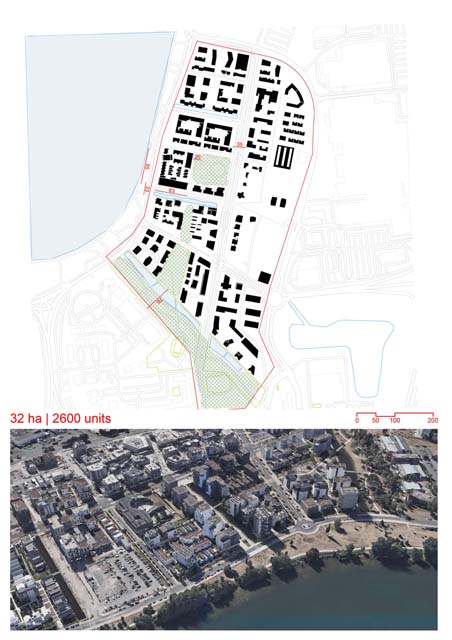
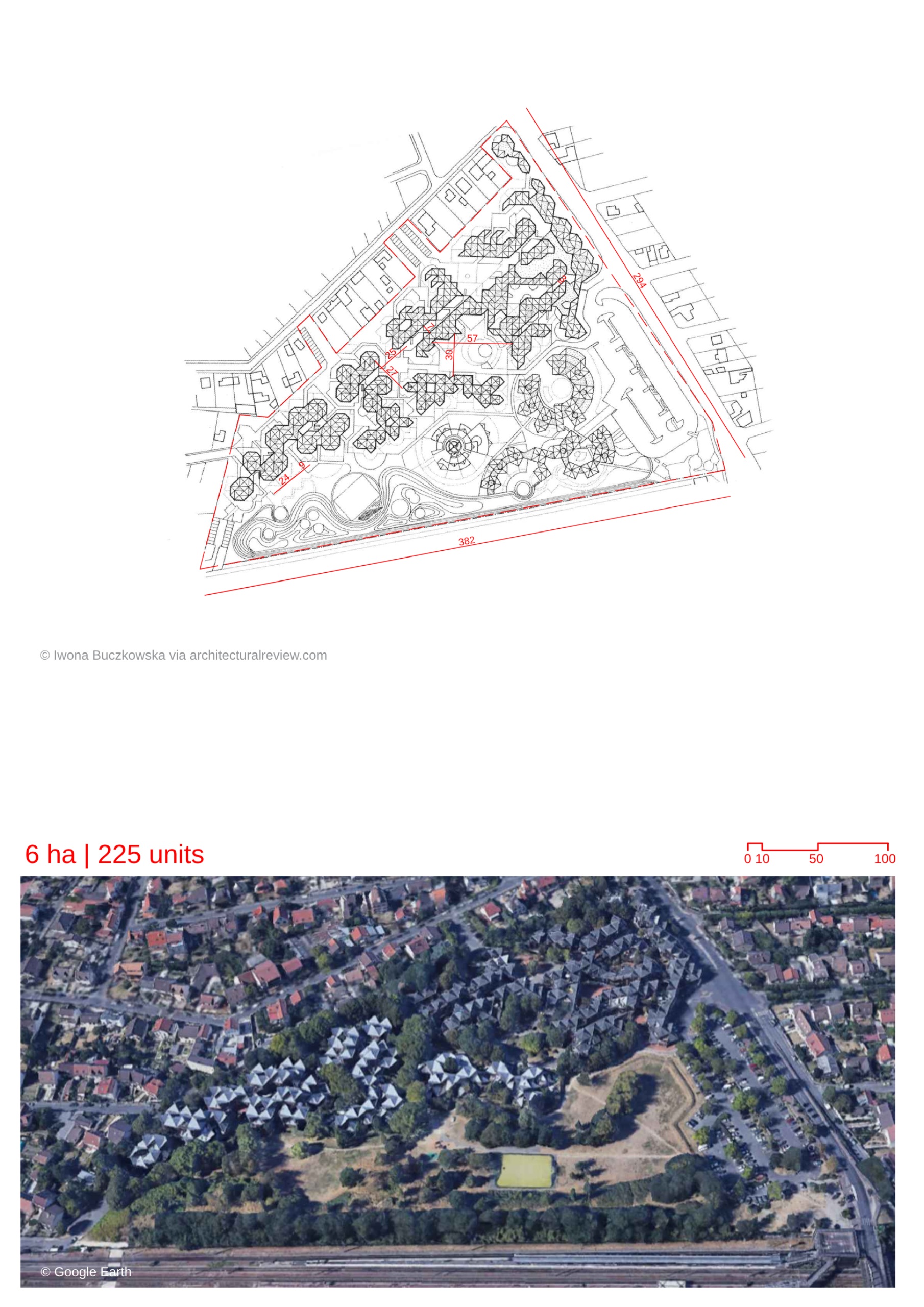
Site area
60000 sqm
Gfa
34000
sqm
Density
1 far
Population density
86
inh/ha
Home Units:
225
Jobs
0
Streetsroad:
0
%
Buildup:
19
%
NonBuild-up:
81 %
Residential
90 %
Business
0
%
Commercial
5
%
Civic
5
%
Description
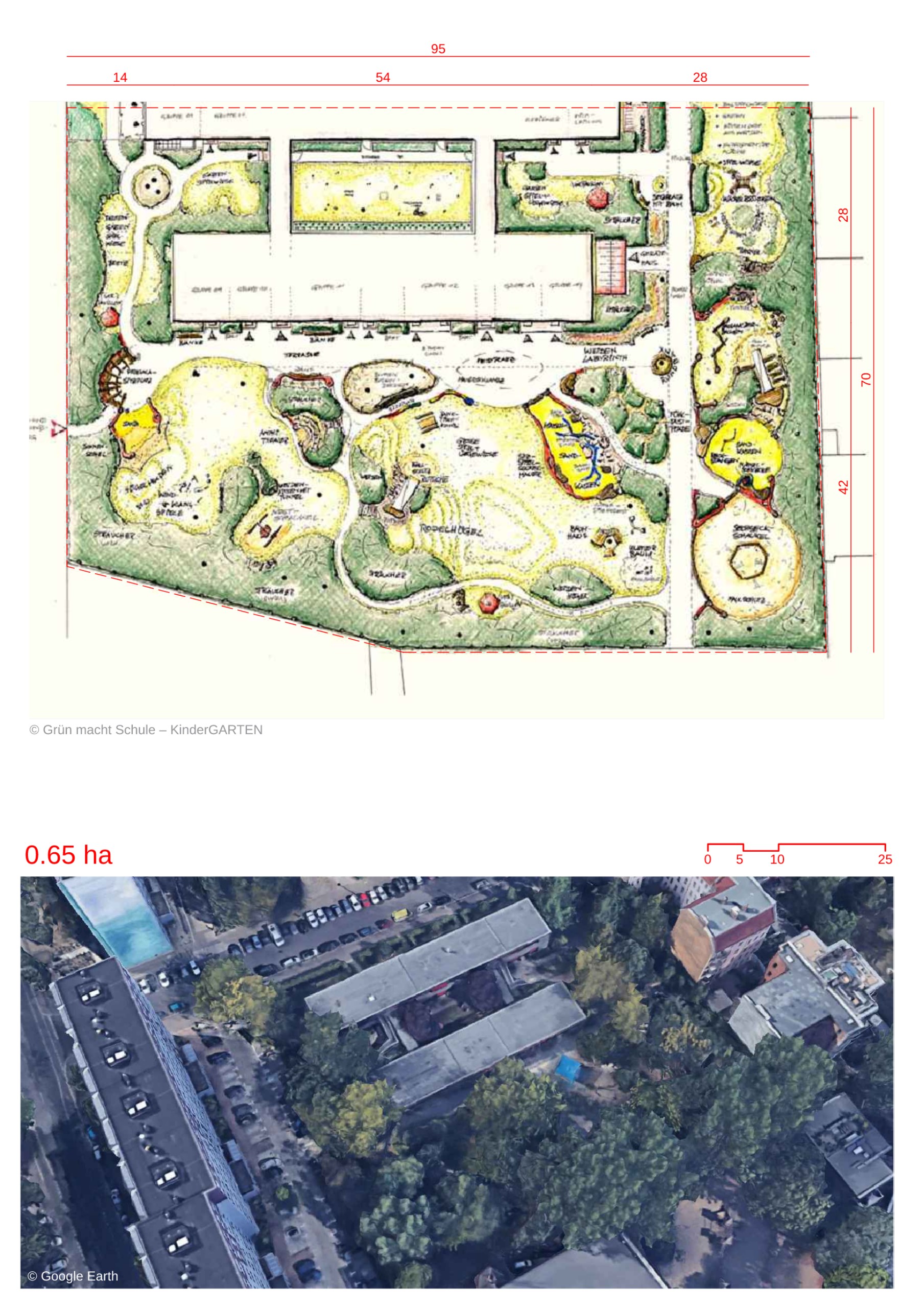
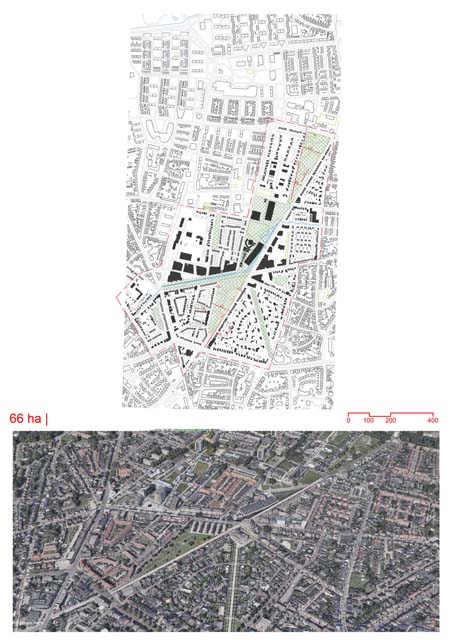
- The project is the largest wooden co-housing development in France and is inspired by the urban form of older cities, which were irregular yet responsive to human scale and interaction.
- The design deviates from the orthogonal grid, opting for a more organic, human-scaled approach to urban form.
- Inspired by the "proliferative" movement of French architect Jean Renaudie, the design emphasizes ecology, community building, and the avoidance of standardization.
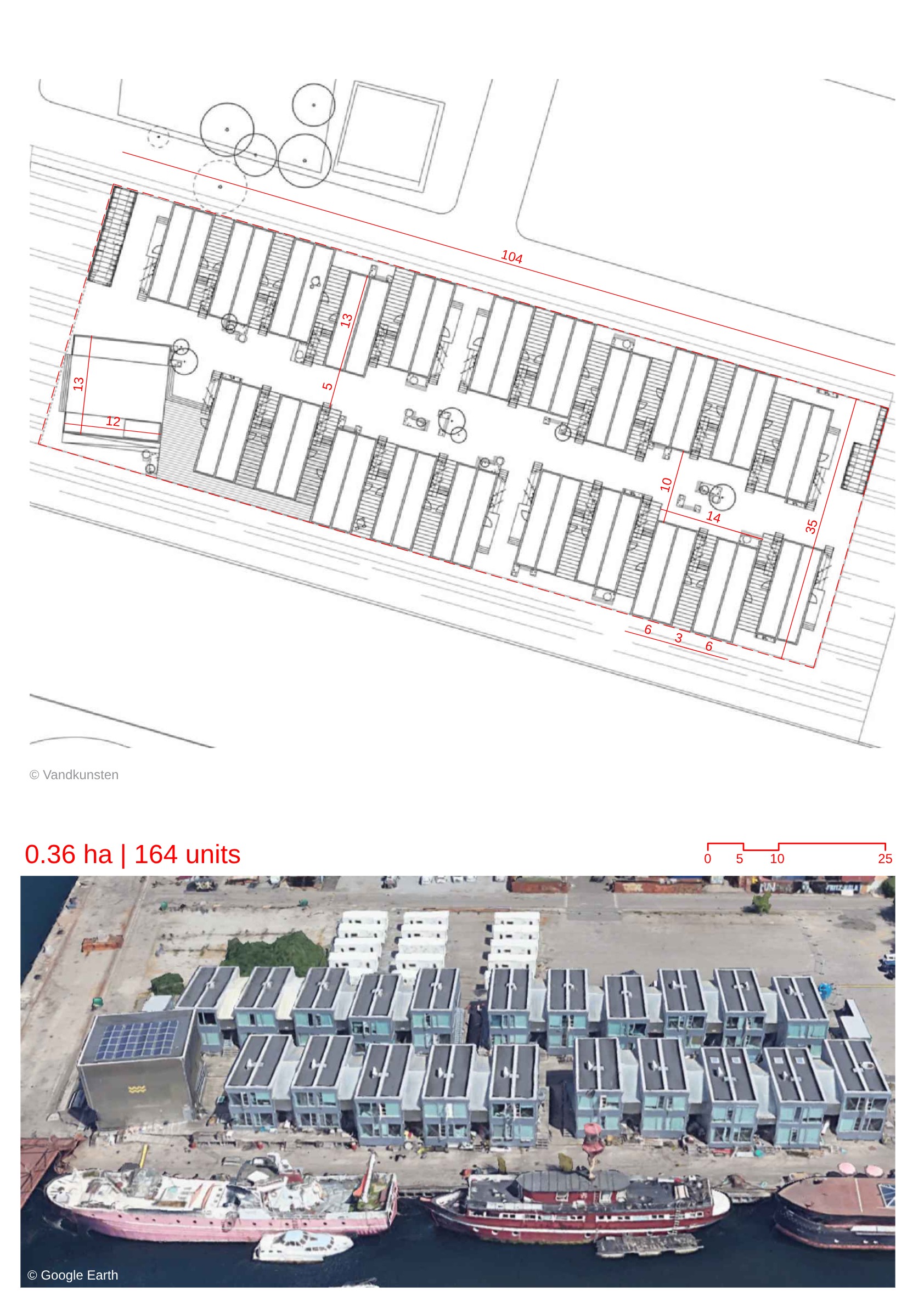
- The architectural layout uses a square module of 4.9 meters arranged diagonally, creating a triangular, jagged volume for the buildings.
- The district is designed to be primarily car-free, with underground and peripheral car parking.
- The ground floor includes a network of pedestrian paths and passageways, while narrow bridge-like passageways connect buildings on the first floor.
- Shops and artist-in-residence workshops are integrated into the ground floor, enriching the public realm.
- Public squares and open spaces, including a Zen garden, are planted with seasonally-changing trees like lime and maple, providing a dynamic natural setting within the district.
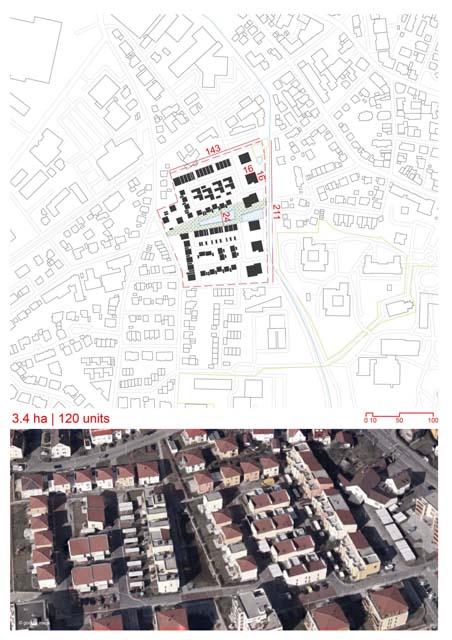
- While the project promotes collective living, emphasis is placed on maintaining a sense of individuality for each home. This is achieved through individual gardens, terraces, and ample daylight.
- A few apartment types have been designed by manipulating the diagonal module, allowing flexibility for different resident needs.
- The development utilizes larch for facades and glue-laminated fir for beams, creating strong yet lightweight structures.
- The use of wood has ecological importance, with its low embodied carbon, contributing to carbon storage and promoting good forest management.
- Timber also provides good thermal insulation, enhancing the energy efficiency of the homes.
Urban Design and Layout
Architectural Inspiration and Principles
Circulation and Connectivity
Public Spaces and Landscaping
Housing and Individuality
Sustainability and Materiality
Location
Deep Dive
Explore a dynamic and data-rich visualization of this masterplan through an embedded Aino.World interactive map. This feature provides a detailed spatial representation of the development, with color-coded information layers highlighting: Buildings – categorized by function and usage ; Green Areas – parks, public spaces, and ecological zones; Points of Interest (POI) – key landmarks, amenities, and services. This map allows users to navigate through the masterplan intuitively, gaining insights into the urban fabric, land use distribution, and connectivity of the area. Dive into the details and analyze how different elements interact within the cityscape.
Sources
Explore more Masterplans
|